We present the first results of JWST Cycle 1 and 2 observations of Sgr A* using NIRCam taken simultaneously at 2.1 and 4.8 μm for a total of ~48 hr over seven different epochs in 2023 and 2024. We find correlated variability at 2.1 and 4.8 μm in all epochs, continual short-timescale (a few seconds) variability, and epoch-to-epoch variable emission implying long-term (~days to months) variability of Sgr A*. A highlight of this analysis is the evidence for subminute, horizon-scale time variability of Sgr A*, probing inner accretion disk size scales. The power spectra of the light curves in each observing epoch also indicate long-term variable emission. With continuous observations, JWST data suggest that the flux of Sgr A* is fluctuating constantly. The flux density correlation exhibits a distinct break in the slope at ~3 mJy at 2.1 μm. The analysis indicates two different processes contributing to the variability of Sgr A*. Brighter emission trends toward shallower spectral indices than the fainter emission. Cross-correlation of the light curves indicates for the first time a time delay of 3–40 s in the 4.8 μm variability with respect to 2.1 μm. This phase shift leads to loops in plots of flux density versus spectral index as the emission rises and falls. Modeling suggests that the synchrotron emission from the evolving, age-stratified electron population reproduces the shape of the observed light curves with a direct estimate of the magnetic field strengths in the range between 40 and 90 G and an upper cutoff energy, Ec, between 420 and 720 MeV.

The American Astronomical Society (AAS), established in 1899 and based in Washington, DC, is the major organization of professional astronomers in North America. Its membership of about 7,000 individuals also includes physicists, mathematicians, geologists, engineers, and others whose research and educational interests lie within the broad spectrum of subjects comprising contemporary astronomy. The mission of the AAS is to enhance and share humanity's scientific understanding of the universe.

The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a leading scientific society promoting physics and bringing physicists together for the benefit of all. It has a worldwide membership of around 50 000 comprising physicists from all sectors, as well as those with an interest in physics. It works to advance physics research, application and education; and engages with policy makers and the public to develop awareness and understanding of physics. Its publishing company, IOP Publishing, is a world leader in professional scientific communications.
A publishing partnership
The Astrophysical Journal Letters is an open access express scientific journal that allows astrophysicists to rapidly publish short notices of significant original research. ApJL articles are timely, high-impact, and broadly understandable.
GOLD OPEN ACCESS FROM 1 JANUARY 2022
F. Yusef-Zadeh et al 2025 ApJL 980 L35
Caitlyn Nojiri et al 2025 ApJL 979 L18
The Earth sits inside a 300 pc-wide void that was carved by a series of supernova explosions that went off tens of millions of years ago, pushing away interstellar gas and creating a bubble-like structure. The 60Fe peak deposits found in the deep-sea crust have been interpreted by the imprints left by the ejecta of supernova explosions occurring about 2–3 and 5–6 Myr ago. It is likely that the 60Fe peak at about 2–3 Myr originated from a supernova occurring in the Upper Centaurus Lupus association in Scorpius Centaurus (≈140 pc) or the Tucana-Horologium association (≈70 pc), whereas the ≈5–6 Myr peak is likely attributed to the solar system's entrance into the bubble. In this Letter, we show that the supernova source responsible for synthesizing the 60Fe peak deposits ≈2–3 Myr ago can consistently explain the cosmic-ray spectrum and the large-scale anisotropy between 100 TeV and 100 PeV. The cosmic-ray knee could then potentially be attributed entirely to a single nearby "PeVatron" source. Matching the intensity and shape of the cosmic-ray spectrum allows us to place stringent constraints on the cosmic-ray energy content from the supernova as well as on the cosmic-ray diffusion coefficient. Making use of such constraints, we provide a robust estimate of the temporal variation of terrestrial ionizing cosmic radiation levels and discuss their implications in the development of early life on Earth by plausibly influencing the mutation rate and, as such, conceivably assisting in the evolution of complex organisms.
Ritvik Basant et al 2025 ApJL 982 L1
Barnard's Star is an old, single M dwarf star that comprises the second-closest extrasolar system. It has a long history of claimed planet detections from both radial velocities and astrometry. However, none of these claimed detections have so far withstood further scrutiny. Continuing this story, extreme precision radial velocity measurements from the ESPRESSO instrument have recently been used to identify four new sub-Earth-mass planet candidates around Barnard's Star. We present here 112 radial velocities of Barnard's Star from the MAROON-X instrument that were obtained independently to search for planets around this compelling object. The data have a typical precision of 30 cm s−1 and are contemporaneous with the published ESPRESSO measurements (2021–2023). The MAROON-X data on their own confirm planet b (P = 3.154 days) and planet candidates c and d (P = 4.124 and 2.340 days, respectively). Furthermore, adding the MAROON-X data to the ESPRESSO data strengthens the evidence for planet candidate e (P = 6.739 days), thus leading to its confirmation. The signals from all four planets are <50 cm s−1, the minimum masses of the planets range from 0.19 to 0.34 M⊕, and the system is among the most compact known among late M dwarfs hosting low-mass planets. The current data rule out planets with masses >0.57 M⊕ (with a 99% detection probability) in Barnard's Star's habitable zone (P = 10–42 days).
Allison M. McCarthy et al 2025 ApJL 981 L22
Isolated planetary-mass objects share their mass range with planets but do not orbit a star. They lack the necessary mass to support fusion in their cores and thermally radiate their heat from formation as they cool, primarily at infrared wavelengths. Many isolated planetary-mass objects show variations in their infrared brightness consistent with nonuniform atmospheric features modulated by their rotation. SIMP J013656.5+093347.3 is a rapidly rotating isolated planetary-mass object, and previous infrared monitoring suggests complex atmospheric features rotating in and out of view. The physical nature of these features is not well understood, with clouds, temperature variations, thermochemical instabilities, and infrared-emitting aurora all proposed as contributing mechanisms. Here we report JWST time-resolved low-resolution spectroscopy from 0.8 to 11 μm of SIMP J013656.5+093347.3, which supports the presence of three specific features in the atmosphere: clouds, hot spots, and changing carbon chemistry. We show that no single mechanism can explain the variations in the time-resolved spectra. When combined with previous studies of this object indicating patchy clouds and aurorae, these measurements reveal the rich complexity of the atmosphere of SIMP J013656.5+093347.3. Gas giant planets in the solar system, specifically Jupiter and Saturn, also have multiple cloud layers and high-altitude hot spots, suggesting these phenomena are also present in worlds both within and beyond our solar system.
Adam G. Riess et al 2024 ApJL 962 L17
We present high-definition observations with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) of >1000 Cepheids in a geometric anchor of the distance ladder, NGC 4258, and in five hosts of eight Type Ia supernovae, a far greater sample than previous studies with JWST. These galaxies individually contain the largest samples of Cepheids, an average of >150 each, producing the strongest statistical comparison to those previously measured with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in the near-infrared (NIR). They also span the distance range of those used to determine the Hubble constant with HST, allowing us to search for a distance-dependent bias in HST measurements. The superior resolution of JWST negates crowding noise, the largest source of variance in the NIR Cepheid period–luminosity relations (Leavitt laws) measured with HST. Together with the use of two epochs to constrain Cepheid phases and three filters to remove reddening, we reduce the dispersion in the Cepheid P–L relations by a factor of 2.5. We find no significant difference in the mean distance measurements determined from HST and JWST, with a formal difference of −0.01 ± 0.03 mag. This result is independent of zero-points and analysis variants including metallicity dependence, local crowding, choice of filters, and slope of the relations. We can reject the hypothesis of unrecognized crowding of Cepheid photometry from HST that grows with distance as the cause of the "Hubble tension" at 8.2σ, i.e., greater confidence than that of the Hubble tension itself. We conclude that errors in photometric measurements of Cepheids across the distance ladder do not significantly contribute to the tension.
The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration et al 2019 ApJL 875 L1
When surrounded by a transparent emission region, black holes are expected to reveal a dark shadow caused by gravitational light bending and photon capture at the event horizon. To image and study this phenomenon, we have assembled the Event Horizon Telescope, a global very long baseline interferometry array observing at a wavelength of 1.3 mm. This allows us to reconstruct event-horizon-scale images of the supermassive black hole candidate in the center of the giant elliptical galaxy M87. We have resolved the central compact radio source as an asymmetric bright emission ring with a diameter of 42 ± 3 μas, which is circular and encompasses a central depression in brightness with a flux ratio ≳10:1. The emission ring is recovered using different calibration and imaging schemes, with its diameter and width remaining stable over four different observations carried out in different days. Overall, the observed image is consistent with expectations for the shadow of a Kerr black hole as predicted by general relativity. The asymmetry in brightness in the ring can be explained in terms of relativistic beaming of the emission from a plasma rotating close to the speed of light around a black hole. We compare our images to an extensive library of ray-traced general-relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations of black holes and derive a central mass of M = (6.5 ± 0.7) × 109 M⊙. Our radio-wave observations thus provide powerful evidence for the presence of supermassive black holes in centers of galaxies and as the central engines of active galactic nuclei. They also present a new tool to explore gravity in its most extreme limit and on a mass scale that was so far not accessible.
Imad Pasha et al 2025 ApJL 980 L3
We report the discovery and multiwavelength follow-up of LEDA 1313424 ("Bullseye"), a collisional ring galaxy (CRG) with nine readily identified rings—the most so far reported for a CRG. These data shed new light on the rapid, multiring phase of CRG evolution. Using Hubble Space Telescope (HST) imaging, we identify and measure nine ring structures, several of which are "piled up" near the center of the galaxy, while others extend to tens of kiloparsecs scales. We also identify faint patches of emission at large radii (~70 kpc) in the HST imaging and confirm the association of this emission with the galaxy via spectroscopy. Deep ground-based imaging using the Dragonfly Telephoto Array finds evidence that this patch of emission is part of an older, fading ring from the collision. We find that the locations of the detected rings are an excellent match to predictions from analytic theory if the galaxy was a 10-ring system whose outermost ring has faded away. We identify the likely impacting galaxy via Keck/KCWI spectroscopy, finding evidence for gas extending between it and the Bullseye. The overall size of this galaxy rivals that of known giant low surface brightness galaxies (GLSBs) such as Malin I, lending credence to the hypothesis that CRGs can evolve into GLSBs as their rings expand and fade. Analysis of the H i content in this galaxy from ALFALFA finds significantly elevated neutral hydrogen with respect to the galaxy's stellar mass, another feature in alignment with GLSB systems.
B. P. Abbott et al 2017 ApJL 848 L12
On 2017 August 17 a binary neutron star coalescence candidate (later designated GW170817) with merger time 12:41:04 UTC was observed through gravitational waves by the Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo detectors. The Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor independently detected a gamma-ray burst (GRB 170817A) with a time delay of  with respect to the merger time. From the gravitational-wave signal, the source was initially localized to a sky region of 31 deg2 at a luminosity distance of
with respect to the merger time. From the gravitational-wave signal, the source was initially localized to a sky region of 31 deg2 at a luminosity distance of 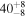 Mpc and with component masses consistent with neutron stars. The component masses were later measured to be in the range 0.86 to 2.26
Mpc and with component masses consistent with neutron stars. The component masses were later measured to be in the range 0.86 to 2.26  . An extensive observing campaign was launched across the electromagnetic spectrum leading to the discovery of a bright optical transient (SSS17a, now with the IAU identification of AT 2017gfo) in NGC 4993 (at
. An extensive observing campaign was launched across the electromagnetic spectrum leading to the discovery of a bright optical transient (SSS17a, now with the IAU identification of AT 2017gfo) in NGC 4993 (at 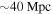 ) less than 11 hours after the merger by the One-Meter, Two Hemisphere (1M2H) team using the 1 m Swope Telescope. The optical transient was independently detected by multiple teams within an hour. Subsequent observations targeted the object and its environment. Early ultraviolet observations revealed a blue transient that faded within 48 hours. Optical and infrared observations showed a redward evolution over ∼10 days. Following early non-detections, X-ray and radio emission were discovered at the transient's position
) less than 11 hours after the merger by the One-Meter, Two Hemisphere (1M2H) team using the 1 m Swope Telescope. The optical transient was independently detected by multiple teams within an hour. Subsequent observations targeted the object and its environment. Early ultraviolet observations revealed a blue transient that faded within 48 hours. Optical and infrared observations showed a redward evolution over ∼10 days. Following early non-detections, X-ray and radio emission were discovered at the transient's position 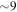 and
and 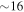 days, respectively, after the merger. Both the X-ray and radio emission likely arise from a physical process that is distinct from the one that generates the UV/optical/near-infrared emission. No ultra-high-energy gamma-rays and no neutrino candidates consistent with the source were found in follow-up searches. These observations support the hypothesis that GW170817 was produced by the merger of two neutron stars in NGC 4993 followed by a short gamma-ray burst (GRB 170817A) and a kilonova/macronova powered by the radioactive decay of r-process nuclei synthesized in the ejecta.
days, respectively, after the merger. Both the X-ray and radio emission likely arise from a physical process that is distinct from the one that generates the UV/optical/near-infrared emission. No ultra-high-energy gamma-rays and no neutrino candidates consistent with the source were found in follow-up searches. These observations support the hypothesis that GW170817 was produced by the merger of two neutron stars in NGC 4993 followed by a short gamma-ray burst (GRB 170817A) and a kilonova/macronova powered by the radioactive decay of r-process nuclei synthesized in the ejecta.
Soumya Roy et al 2025 ApJL 981 L19
Solar flares are regularly observed in extreme-ultraviolet soft X-rays (SXRs) and hard X-rays (HXRs). However, those in near- and mid-ultraviolet are sparse. The Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) on board the Aditya-L1, launched on 2023 September 2, provides regular observations in the 200–400 nm wavelength range through 11 filters. Here, we report the observation of the X6.3 flare on 2024 February 22 using eight narrowband (NB) filters of SUIT. We have also used co-spatiotemporal observations from Solar Dynamics Observatory/Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (SDO/AIA), Solar Orbiter/STIX, GONG Hα, Aditya-L1/SoLEXS, and GOES. We obtained light curves over the flaring region from AIA 1600 and 1700 Å and GONG Hα and compared them with the disk-integrated light curve obtained from GOES and SoLEXS SXRs and STIX HXRs. We find that the flare peaks in SUIT NB01, NB03, NB04, and NB08 filters simultaneously with HXRs 1600 and 1700 Å, along with the peak temperature obtained from SoLEXS. In contrast, in NB02 and NB05, the flare peaks ∼2 min later than the HXR peak, while in NB06 and NB07, the flare peaks ∼3 min after the GOES SXR peak. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first observation of a flare in these wavelengths (except in NB03, NB04, and NB05). Moreover, for the first time, we show the presence of a bright kernel in NB02. These results demonstrate the capabilities of SUIT observations in flare studies.
A. Marino et al 2025 ApJL 980 L36
On 2024 May 27, the Wide-field X-ray Telescope on board the Space Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Einstein Probe (EP) mission detected enhanced X-ray emission from a new transient source in the Small Magellanic Cloud during its commissioning phase. Prompt follow-up with the EP Follow-up X-ray Telescope, the Swift X-ray Telescope. and NICER have revealed a very soft, thermally emitting source (kT ~ 0.1 keV at the outburst peak) with an X-ray luminosity of L ~ 4 × 1038 erg s−1, labeled EP J005245.1−722843. This supersoft outburst faded very quickly in a week's time. Several emission lines and absorption edges were present in the X-ray spectrum, including deep nitrogen (0.67 keV) and oxygen (0.87 keV) absorption edges. The X-ray emission resembles the supersoft source phase of typical nova outbursts from an accreting white dwarf (WD) in a binary system, despite the X-ray source being historically associated with an O9-B0e massive star exhibiting a 17.55 day periodicity in the optical band. The discovery of this supersoft outburst suggests that EP J005245.1−722843 is a BeWD X-ray binary: an elusive evolutionary stage where two main-sequence massive stars have undergone a common envelope phase and experienced at least two episodes of mass transfer. In addition, the very short duration of the outburst and the presence of Ne features hint at a rather massive, i.e., close to the Chandrasekhar limit, Ne–O WD in the system.
Dazhi Zhou et al 2025 ApJL 982 L17
We present Atacama Compact Array (ACA) Band-3 observations of the protocluster SPT2349−56, an extreme system hosting >10 ultraluminous infrared galaxies (ULIRGs; LIR ≳ 1012L⊙) in a 200 kpc diameter region at z = 4.3, to study its integrated molecular gas content via CO(4–3) and the long-wavelength dust continuum. The ∼30 hr integration represents one of the longest exposures yet taken on a single pointing with the ACA 7 m. The low-resolution ACA data (21 0 × 12
0 × 12 2) reveal a 75% excess CO(4–3) flux compared to the sum of individual sources detected in higher-resolution Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) data (1
2) reveal a 75% excess CO(4–3) flux compared to the sum of individual sources detected in higher-resolution Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) data (1 0 × 0
0 × 0 8). Our work also reveals a similar result by tapering the ALMA data to 10''. In contrast, the 3.2 mm dust continuum shows little discrepancy between ACA and ALMA. A single-dish [C ii] spectrum obtained by APEX/FLASH supports the ACA CO(4–3) result, revealing a large excess in [C ii] emission relative to ALMA. The missing flux is unlikely due to undetected faint sources but instead suggests that high-resolution ALMA observations might miss extended and low-surface-brightness gas. Such emission could originate from the circumgalactic medium or the preheated protointracluster medium (proto-ICM). If this molecular gas reservoir replenishes the star formation fuel, the overall depletion timescale will exceed 400 Myr, reducing the requirement for the simultaneous ULIRG activity in SPT2349−56. Our results highlight the role of an extended gas reservoir in sustaining a high star formation rate in SPT2349−56 and potentially establishing the ICM during the transition phase to a mature cluster.
8). Our work also reveals a similar result by tapering the ALMA data to 10''. In contrast, the 3.2 mm dust continuum shows little discrepancy between ACA and ALMA. A single-dish [C ii] spectrum obtained by APEX/FLASH supports the ACA CO(4–3) result, revealing a large excess in [C ii] emission relative to ALMA. The missing flux is unlikely due to undetected faint sources but instead suggests that high-resolution ALMA observations might miss extended and low-surface-brightness gas. Such emission could originate from the circumgalactic medium or the preheated protointracluster medium (proto-ICM). If this molecular gas reservoir replenishes the star formation fuel, the overall depletion timescale will exceed 400 Myr, reducing the requirement for the simultaneous ULIRG activity in SPT2349−56. Our results highlight the role of an extended gas reservoir in sustaining a high star formation rate in SPT2349−56 and potentially establishing the ICM during the transition phase to a mature cluster.
Su Wang et al 2025 ApJL 982 L15
The WASP-47 system is notable as the first known system hosting both inner and outer low-mass planetary companions around a hot Jupiter, with an ultra-short-period (USP) planet as the innermost planetary companion. The formation of such a unique configuration poses challenges to the lonely hot Jupiter formation model. Hot Jupiters in multiple planetary systems may have a similar formation process with warm Jupiter systems, which are more commonly found with companions. This implies that the WASP-47 system could bridge our understanding of both hot and warm Jupiter formation. In this work, we propose a possible formation scenario for the WASP-47 system based on its orbital configuration. The mean motion resonance trapping, giant planet perturbations, and tidal effects caused by the central star are key factors in the formation of USP planets in multiple planetary systems with hot Jupiters. Whether a planet can become a USP planet or a short-period super-Earth planet depends on the competition between eccentricity excitation by nearby giant planet perturbations and the eccentricity damping due to tidal effects. The  value of the innermost planet is essential for the final planetary configuration. Our results suggest that a
value of the innermost planet is essential for the final planetary configuration. Our results suggest that a  in the range of [1, 10] is favorable for the formation of the WASP-47 system. Based on the formation scenario, we estimate an occurrence rate of 8.4% ± 2.4% for USP planets in systems similar to WASP-47.
in the range of [1, 10] is favorable for the formation of the WASP-47 system. Based on the formation scenario, we estimate an occurrence rate of 8.4% ± 2.4% for USP planets in systems similar to WASP-47.
Govind Nandakumar et al 2025 ApJL 982 L14
An important step in understanding the formation and evolution of the nuclear star cluster (NSC) is to investigate its chemistry and chemical evolution. Additionally, exploring the NSC's relationship to the other structures in the Galactic center and the Milky Way disks is of great interest. Extreme optical extinction has previously prevented optical studies, but near-IR high-resolution spectroscopy is now possible. Here, we present a detailed chemical abundance analysis of 19 elements—more than 4 times as many as previously published—for nine stars in the NSC of the Milky Way, observed with the Immersion GRating INfrared Spectrometer on the Gemini South telescope. This study provides new, crucial observational evidence to shed light on the origin of the NSC. We demonstrate that it is possible to probe a variety of nucleosynthetic channels, reflecting different chemical evolution timescales. Our findings reveal that the NSC trends for the elements F, Mg, Al, Si, S, K, Ca, Ti, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn, as well as for the s-process elements Ba, Ce, Nd, and Yb, generally follow the inner-bulge trends within uncertainties. This suggests a likely shared evolutionary history, and our results indicate that the NSC population is consistent with the chemical sequence observed in the inner Galaxy (the inner-disk sequence). However, we identify a significant and unexplained difference in the form of higher Na abundances in the NSC compared to the inner bulge. This is also observed in few Galactic globular clusters and may suggest a common enrichment process at work in all these systems.
Ke Fang et al 2025 ApJL 982 L16
A neutrino-like event with an energy of ∼220 PeV was recently detected by the KM3NeT/ARCA telescope. If this neutrino comes from an astrophysical source or from the interaction of an ultrahigh-energy cosmic ray in the intergalactic medium, the ultrahigh-energy gamma rays that are coproduced with the neutrinos will scatter with the extragalactic background light, producing an electromagnetic cascade and resulting in emission at GeV-to-TeV energies. In this Letter, we compute the gamma-ray flux from this neutrino source considering various source distances and strengths of the intergalactic magnetic field (IGMF). We find that the associated gamma-ray emission could be observed by existing imaging air Cherenkov telescopes and air shower gamma-ray observatories, unless the strength of the IGMF is B ≳ 3 × 10−13 G or the ultrahigh-energy gamma rays are attenuated inside of the source itself. In the latter case, this source is expected to be radio-loud.
Suinan Zhang et al 2025 ApJL 982 L10
We present the highest-resolution (∼0 04) Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array 1.3 mm continuum observations so far of three massive star-forming clumps in the Central Molecular Zone (CMZ), namely 20 km s−1 C1, 20 km s−1 C4, and Sgr C C4, which reveal prevalent compact millimeter emission. We extract the compact emission with astrodendro and identify a total of 199 fragments with a typical size of ∼370 au, which represent the first sample of candidates of protostellar envelopes and disks and kernels of prestellar cores in these clumps that are likely forming star clusters. Compared with the protoclusters in the Galactic disk, the three protoclusters display a higher level of hierarchical clustering, likely a result of the stronger turbulence in the CMZ clumps. Compared with the mini-starbursts in the CMZ, Sgr B2 M and N, the three protoclusters also show stronger subclustering in conjunction with a lack of massive fragments. The efficiency of high-mass star formation of the three protoclusters is on average 1 order of magnitude lower than that of Sgr B2 M and N, despite a similar overall efficiency of converting gas into stars. The lower efficiency of high-mass star formation in the three protoclusters is likely attributed to hierarchical cluster formation.
04) Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array 1.3 mm continuum observations so far of three massive star-forming clumps in the Central Molecular Zone (CMZ), namely 20 km s−1 C1, 20 km s−1 C4, and Sgr C C4, which reveal prevalent compact millimeter emission. We extract the compact emission with astrodendro and identify a total of 199 fragments with a typical size of ∼370 au, which represent the first sample of candidates of protostellar envelopes and disks and kernels of prestellar cores in these clumps that are likely forming star clusters. Compared with the protoclusters in the Galactic disk, the three protoclusters display a higher level of hierarchical clustering, likely a result of the stronger turbulence in the CMZ clumps. Compared with the mini-starbursts in the CMZ, Sgr B2 M and N, the three protoclusters also show stronger subclustering in conjunction with a lack of massive fragments. The efficiency of high-mass star formation of the three protoclusters is on average 1 order of magnitude lower than that of Sgr B2 M and N, despite a similar overall efficiency of converting gas into stars. The lower efficiency of high-mass star formation in the three protoclusters is likely attributed to hierarchical cluster formation.
